Glioblastoma
March 2nd, 2021
Glioblastomas (malignant glioma) are the most common adult malignant brain tumors, and 20% of all primary brain neoplasms are glioblastoma multiforme tumors. Mortality associated with GBM is greater than 90% at 5 years, with a median survival of 12.6 months. The prognosis for this tumor is at the extreme worst end because of its high-grade status.
GBM have traditionally been divided into primary and secondary; the former arising de novo (90%) whereas the latter developed from a pre-existing lower grade tumour (10%).GBM can occur at any age, but tends to occur more often in older adults. It can cause worsening headaches, nausea, vomiting and seizures.
Diagnosis:
-Neurological exam
-Imaging tests (CT,MRI)
-Biopsy
Treatment:
-Surgery to remove
-Radiation therapy
-Chemotherapy
-Tumor treating fields (TTF) therapy.
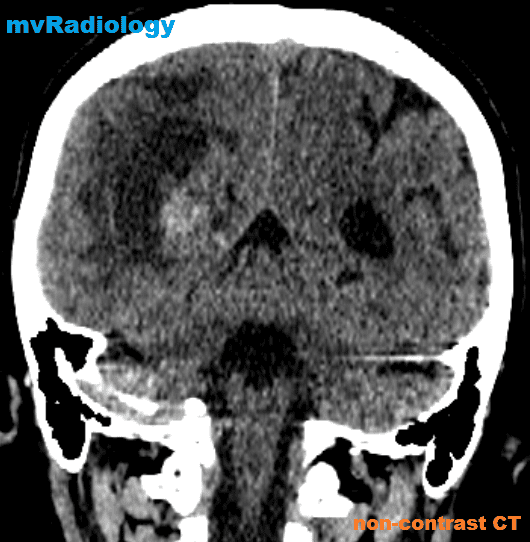
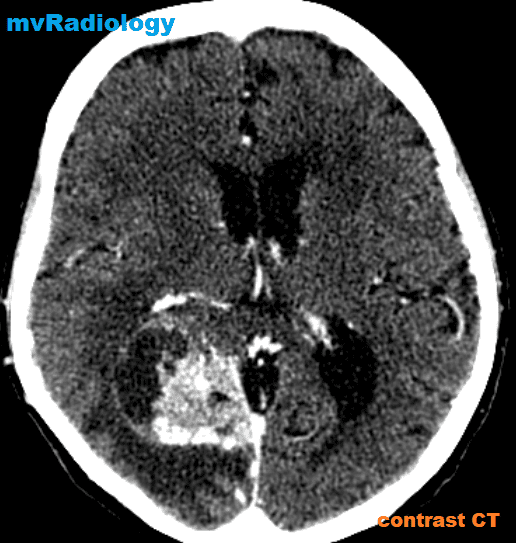
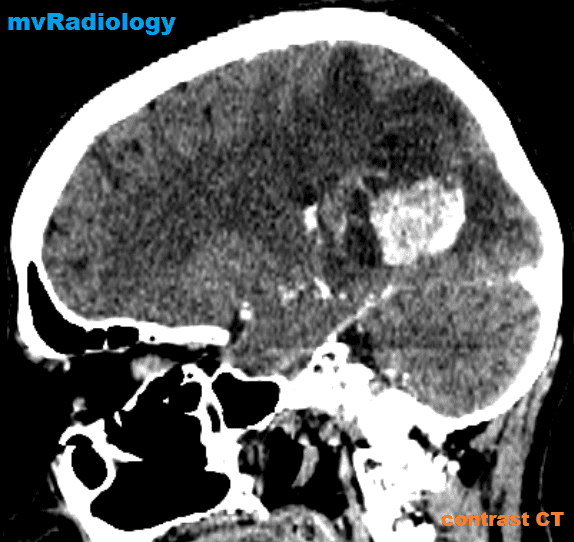
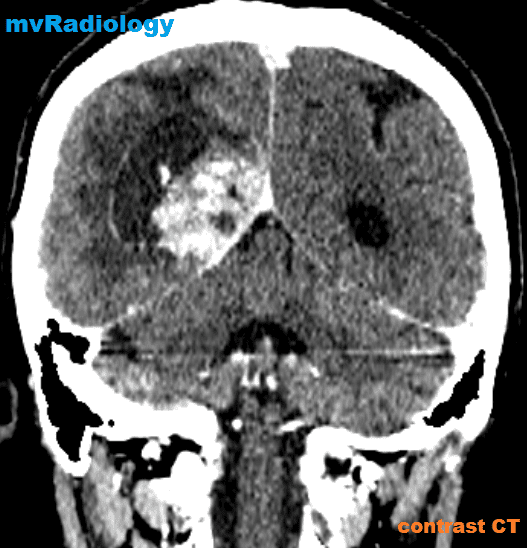
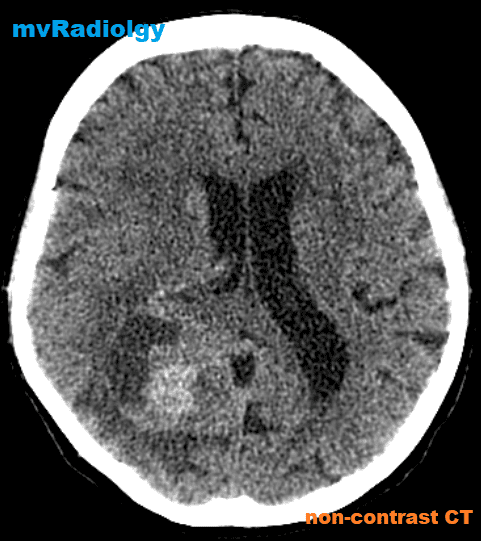
all casesCT:
-irregular thick margins: iso- to slightly hyperattenuating (high cellularity)
-irregular hypodense centre representing necrosis
-marked mass effect
-surrounding vasogenic oedema
-haemorrhage is occasionally seen
-calcification is uncommon
-intense irregular, heterogeneous enhancement of the margins is almost always present.